. In this article, we want to preview the direction TensorFlow’s high-level APIs are heading, and answer some frequently asked questions.
is an extremely popular high-level API for building and training deep learning models. It’s used for fast prototyping, state-of-the-art research, and production. While TensorFlow supports Keras today, with 2.0, we are integrating Keras more tightly into the rest of the TensorFlow platform.
By establishing Keras as the high-level API for TensorFlow, we are making it easier for developers new to machine learning to get started with TensorFlow. A single high-level API reduces confusion and enables us to focus on providing advanced capabilities for researchers.
We hope you’ll enjoy using it as much as we do!
Keras has several key advantages:
- User-friendly: Keras has a simple, consistent interface optimized for common use cases. It provides clear and actionable feedback for user errors, and easy to understand error messages, often with helpful advice.
- Modular and composable: Keras models are made by connecting configurable building blocks together, with few restrictions. Parts of Keras can be reused without having to adopt or even know about everything the framework offers. For instance, you can use layers or optimizers without using a Keras
Model for training.
- Easy to extend: You can write custom building blocks to express new ideas for research, including new layers, loss functions, and [insert your idea here] to develop state-of-the-art ideas.
- For beginners, and for experts: Deep learning developers come from many backgrounds and experience levels, and Keras provides helpful APIs whether you’re just starting out, or whether you have years of experience.
Together, these make workflows easier and more productive across a wide range of use cases, from learning ML, to research, to applications development, to deployment.
First, we’ll answer a couple questions that have come up. Next, we’ll take a closer look at what the version of Keras that comes with TensorFlow enables you to do.
FAQ
I thought Keras was a separate library?
Most of all, Keras is an API spec. A reference implementation of Keras is maintained as an independent open source project, which you can find at
www.keras.io. This project is independent of TensorFlow, and has an active community of contributors and users. TensorFlow includes a full implementation of the Keras API (in the
tf.keras module) with TensorFlow-specific enhancements.
Is Keras just a wrapper for TensorFlow, or other libraries?
Nope, this is a common (but understandable) misconception. Keras is an
API standard for defining and training machine learning models. Keras is not tied to a specific implementation: The Keras API has implementations for TensorFlow, MXNet, TypeScript, JavaScript, CNTK, Theano, PlaidML, Scala, CoreML, and other libraries.
What is the difference between the version of Keras that’s built-in to TensorFlow, and the version I can find at keras.io?
TensorFlow includes an implementation of the Keras API (in the
tf.keras module) with TensorFlow-specific enhancements. These include support for
eager execution for intuitive debugging and fast iteration, support for the TensorFlow SavedModel model exchange format, and integrated support for distributed training, including training on TPUs. Eager execution is especially useful when using the tf.keras
model subclassing API. This API was inspired by
Chainer, and enables you to write the forward pass of your model imperatively. tf.keras is tightly integrated into the TensorFlow ecosystem, and also includes support for:
- tf.data, enabling you to build high performance input pipelines. If you prefer, you can train your models using data in NumPy format, or use tf.data for scale and performance.
- Distribution strategies, for distributing training across a wide variety of compute configurations, including GPUs and TPUs spread across many machines.
- Exporting models. Models created with the tf.keras APIs can be serialized in the TensorFlow SavedModel format, and served using TensorFlow Serving or via other language bindings (Java, Go, Rust, C#, etc.).
- Exported models can be deployed on mobile and embedded devices with TensorFlow Lite, and also work with TensorFlow.js (note: you can also develop models directly in JavaScript using the same familiar Keras API).
- Feature columns, for effectively representing and classifying structured data.
- And more in the works.
How do I install tf.keras? Do I need to also install Keras via pip?
tf.keras is included with TensorFlow. You do not need to separately install Keras. For example, if inside a
Colab notebook you run:
!pip install tensorflow
import tensorflow as tf
Dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense
You will now be using tf.keras. If you’re new to the imports, you can check out some of the recent
tutorials for examples.
You mentioned that TensorFlow offers different API styles for beginners and experts. How do these look?
TensorFlow developers have many experience levels (from students learning ML for the first time, to ML experts and researchers). Likewise, one of the strengths of TensorFlow is that it provides several APIs to support different workflows and goals. Similarly, it is a primary design goal of TensorFlow’s Keras integration that users can pick and choose parts of Keras that they more benefit from without having to adopt the whole framework.
The Sequential API
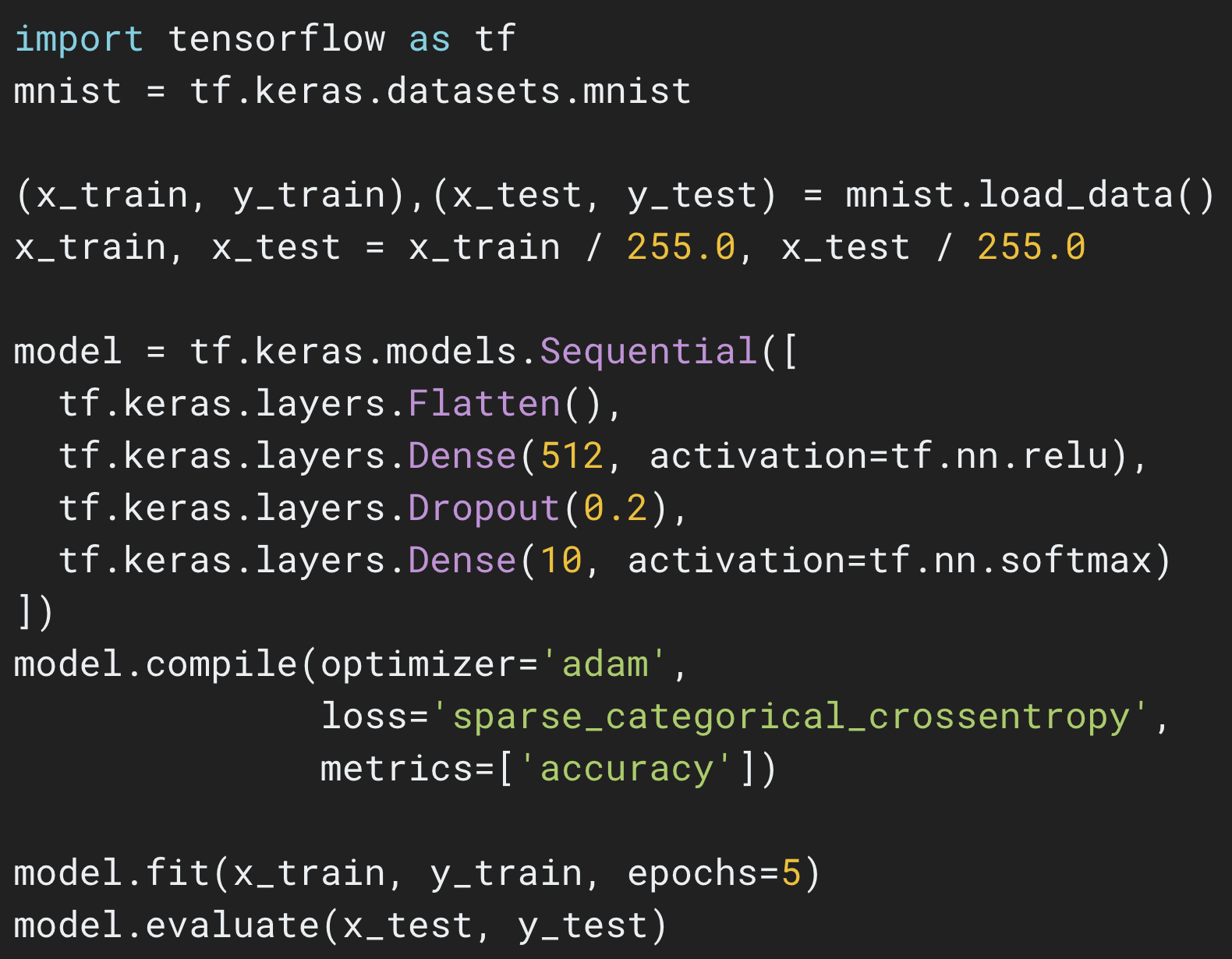 |
| Click here for an example of training your first neural network in just a few lines of code. |
The most common way to define your model is by building a graph of layers, which corresponds to the mental model we normally use when we think about deep learning. The simplest type of model is a stack of layers. You can define such a model using the Sequential API, like this:
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation=’relu’))
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation=’relu’))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation=’softmax’))
Such a model can then be compiled and trained in a few lines:
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’,
loss=’sparse_categorical_crossentropy’,
metrics=[‘accuracy’])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
You can find more examples of using the Sequential API on
tensorflow.org/tutorials under the “Learn and Use ML” section.
 |
| Click here for a tutorial that walks you through training your first neural network on the Fashion MNIST dataset using the Sequential API. |
The Functional API
Of course, a sequential model is a simple stack of layers that cannot represent arbitrary models. More advanced models can be built using the
Functional API, which enables you to define complex topologies, including multi-input and multi-output models, models with shared layers, and models with residual connections.
When building models with the functional API, layers are callable (on a tensor), and return a tensor as output. These input tensor(s) and output tensor(s) can then be used to define a model. For example:
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(32,))
# A layer instance is callable on a tensor, and returns a tensor.
x = layers.Dense(64, activation=’relu’)(inputs)
x = layers.Dense(64, activation=’relu’)(x)
predictions = layers.Dense(10, activation=’softmax’)(x)
# Instantiate the model given inputs and outputs.
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=predictions)
Such a model can be compiled and trained using the same simple commands above. You can learn more about the Functional API
here.
The Model Subclassing API
Fully customizable models can be built by using the
Model Subclassing API, You define your own forward pass imperatively in this style, in the body of a class method. For example:
class MyModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
# Define your layers here.
self.dense_1 = layers.Dense(32, activation=’relu’)
self.dense_2 = layers.Dense(num_classes, activation=’sigmoid’)
def call(self, inputs):
# Define your forward pass here,
# using layers you previously defined in `__init__`
x = self.dense_1(inputs)
return self.dense_2(x)
These models are more flexible, but can be harder to debug. All three types of models can be compiled and trained using the simple compile and fit commands shown earlier, or you can write your own custom training loop for complete control.
For example:
model = MyModel()
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
logits = model(images, training=True)
loss_value = loss(logits, labels)
grads = tape.gradient(loss_value, model.variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.variables))
For more examples in the Model Subclassing style, check out the links below, or visit
tensorflow.org/tutorials (see the “research and experimentation” section).
 |
| A GAN implemented using the Model Subclassing API |
What if my research doesn’t fit into one these styles?
If you find tf.keras restricting for your application area, you have many options. You can:
- Use tf.keras.layers separately from the Keras model definition and write your own gradient and training code.
You can similarly use tf.keras.optimizers, tf.keras.initializers, tf.keras.losses, or tf.keras.metrics separately and independently.
- Ignore tf.keras entirely and use low-level TensorFlow, Python, and AutoGraph to get the results you want.
It’s entirely up to you! Note that the non-Object Oriented layers in tf.layers will be deprecated, and tf.contrib.* (including high-level APIs like tf.contrib.slim and tf.contrib.learn) will not be available in TF 2.0.
What happens to Estimators?
Estimators are extensively used both within Google as well in the broader TensorFlow community. Several models have been packaged as
Premade Estimators, including the Linear Classifier, DNN Classifier, Combined DNN Linear Classifier (aka Wide and Deep Models), and Gradient Boosted Trees. These models are production-ready and widely deployed, and, for all of these reasons, the Estimator APIs, including Premade Estimators will be included in TensorFlow 2.0.
For users of Premade Estimators, the impact of the new focus on Keras and eager execution will be minimal. We may change the implementation of Premade Estimators, while keeping the API surface the same. We will also be working on adding Keras versions of the models implemented as Premade Estimators, and we will extend Keras to better fulfill large scale production requirements.
That said, if you are working on custom architectures, we suggest using tf.keras to build your models instead of Estimator. If you are working with infrastructure that requires Estimators, you can use
model_to_estimator() to convert your model while we work to ensure that Keras works across the TensorFlow ecosystem.
Onward to TensorFlow 2.0!
We hope you’ll enjoy using tf.keras as much as we do! Over the next few months, the TensorFlow team will be focused on polishing the developer experience. Our documentation and tutorials will reflect this path. We look forward to your thoughts and feedback (check out our
community resources), and contributions via GitHub issues and PRs. Thanks everyone!





